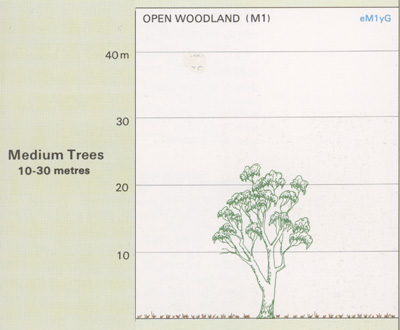
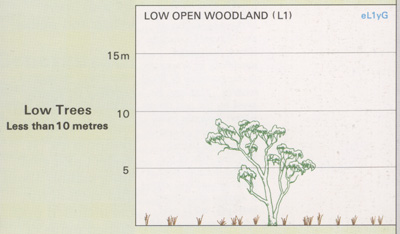
Acacia Open Woodlands
- Usually occur in low to undulating inland
areas, in regions with mainly summer rainfall
in northern Australia, and mainly winter
rainfall in southern Australia.
- Cover extensive areas of the arid zone and drier
tropical north, mostly with a shrubby or grassy
ground layer.
- Dominant acacias include Acacia aneura (Mulga), A. georginae (Georgina Gidgee),
A. tephrina (Boree), A. cambagei (Gidgee),
A. harpophylla (Brigalow), A. peuce (Waddy)
and A. papyrocarpa (Western Myall), with
the most widespread species being Mulga.
- Ground layers are generally herbaceous or chenopod/saltbush shrubs and grasses.
Little of the Acacia Open Woodlands have been cleared. Many areas have been modified by grazing pressure from domestic stock, feral animals and macropods.
![]() Photos from the Australian Plant Image Index
Photos from the Australian Plant Image Index
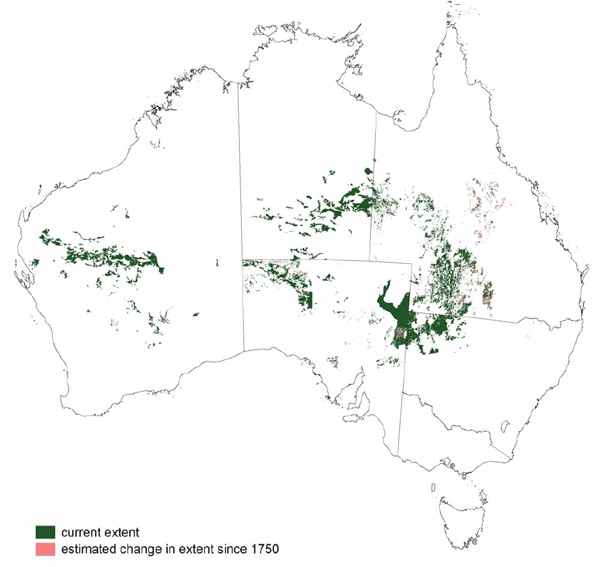
Sources: Australia's Native Vegetation - from rainforest to spinifex, map and information poster produced by the National Land & Water Audit, Natural Heritage Trust, Australian Government, 2001
Map: Australia's Native Vegetation - A summary of Australia's Major Vegetation Groups, 2007, Australian Government website
https://www.environment.gov.au/system/files/resources/a9897cf2-9d38-4201-bea2-13dadf3af9a8/files/major-veg-summary.pdf
Structure diagram: Atlas of Australian Resources - Vol. 6, Vegetation,
AUSLIG, Canberra, 1990
![An Australian Government Initiative [logo]](/images/austgovt_brown_90px.gif)